profile/7350IMG_20200427_212430.jpg
Justin
Malaria Parasite Test
~0.5 mins read
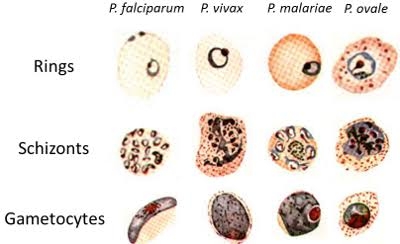
This is a laboratory procedure used to test for the presence of a malaria parasite. Some malaria species include; plasmodium falciparum(kills), plasmodium ovale, plasmodium vivax, plasmodium malariae.
This test can be done with the thin film or the thick film.
The thin film is easier to fix and it shows the parasite shape and size of the red cells. The thick film improves sensitivity.
Staining can be done with either rapid fields method (faster and gives quicker diagnosis) or Giemsa stain(shows a slightly better colour of the parasites and red cell)
Plasmodium falciparum under the microscope can be diagnosed in three main stages. They include; Trophozoite stage, schizont stage and the Gametocyte stage.
profile/7350IMG_20200427_212430.jpg
Justin
The Skeleton
~0.4 mins read
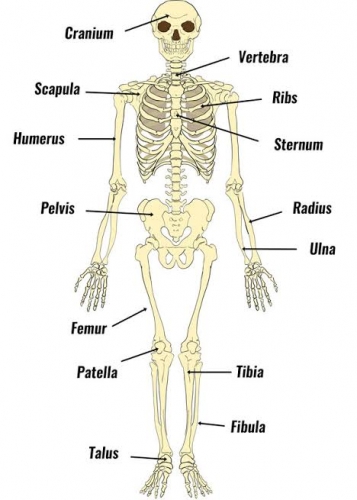
Skeleton Is the bony framework of the body which provides support, shape and protection to the soft tissues and organs in animals. Without skeleton, animals may not be able to move or carry out other life processes.
Types of skeleton
1.hydrostatic(fluid) skeleton: this type of skeleton is possessed by a soft bodied animal.
2.Exoskeleton: this type is found outside or at the external part of the body of some animals.
3.Endoskeleton:this type of skeleton is found inside the body of animals.
Advertisement

Link socials
Matches
Loading...
