profile/9095a1c4934a45b913855bd7f587ff15698d.jpg.webp
Austin
ONTOLOGICAL APPROACH TO MISCARRIAGE
ONTOLOGICAL APPROACH TO MISCARRIAGE
~1.0 mins read
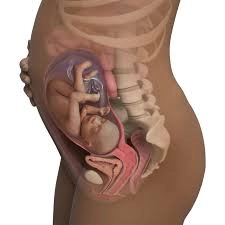
Miscarriage is a significant topic that covers a range of topics, including the philosophical and ontological ramifications of the loss of a pregnancy as well as the psychological, emotional, physical, spiritual, and resultant mental problems suffered by women who have gone through it. A miscarriage occurs most frequently in the first trimester of pregnancy, with an estimated frequency of between 10 and 15% of all clinically recognized pregnancies. The World Health Organisation specifies a miscarriage as the ejection or extraction of an embryo or foetus weighing 500 g or less from the mother. The weight requirement corresponds to a gestational age between 20 and 22 weeks. The event can be extremely upsetting for women and their spouses and is frequently accompanied by emotional suffering and loss. In an effort to comprehend the effects miscarriage has on the individuals who experience it as well as its wider societal ramifications, researchers and philosophers have delved into the ontological elements of miscarriage. Additionally, there have been many conventional ideas that have fallen apart under scrutiny about the cause and care of women who experience miscarriages. In the range of reproductive failure connecting subfertility and late pregnancy problems, research has highlighted the significance of miscarriage. But the major extent of a woman's body's deviations and the existence of chromosomal abnormalities in miscarriages explain the cause of the loss, necessitating medical attention and the adoption of novel tools before pregnancy.
#Scientific Researcher
#Academic Writer
profile/9095a1c4934a45b913855bd7f587ff15698d.jpg.webp
Austin
Fruit And Vegetable: Role Of Phytochemicals In Cancer Prevention
~1.3 mins read
Cancer is a condition marked by abnormal cell proliferation that has the potential to spread to other body organs and invade them. Changes in the genes that control how the body normally functions are one of several elements that contribute to the development of cancer. There is growing interest in various cancer prevention measures as a result of the steadily rising cancer incidence in the world as well as the growing issues with drug resistance. According to estimates, dietary changes could stop one-third of cancer-related fatalities. Phytochemicals, which are found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and other plant foods, can be consumed to increase bioactive compounds and anti-oxidant defenses. This can influence the signal transduction pathways in cells that control cell proliferation and apoptosis as well as prevent, reduce, or delay DNA oxidation. It is suggested that eating lots of fruits and vegetables can lower your chance of developing cancer. When compared to ingestion of just 14 servings per week, a weekly intake of 28 servings of vegetables indicated a 35% reduction in the incidence of prostate cancer. Additionally, eating fruits and vegetables was linked to a lower risk of pancreatic cancer. Dark green vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, yellow vegetables, carrots, beans, onions, and garlic are all found to have a strong inverse relationship. A significant Dutch study, however, found an inverse relationship between fruit and vegetable consumption and a lower risk of colon cancer in women. The likelihood of developing diseases has been found to be adversely linked with regular consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and other plant foods. The amount of fruits and vegetables that Americans and other nations typically consume and what is advised by the 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans differ significantly. The idea is to motivate customers to consume 9 to 13 servings of fruits and vegetables each day in all their varieties. Each day's recommended servings of fruits and vegetables include fresh, processed fruits and vegetables like frozen and canned goods, prepared foods, 100% fruit juices, 100% vegetable juices, and dry fruits.
Advertisement

Link socials
Matches
Loading...
