profile/7350IMG_20200427_212430.jpg
Justin
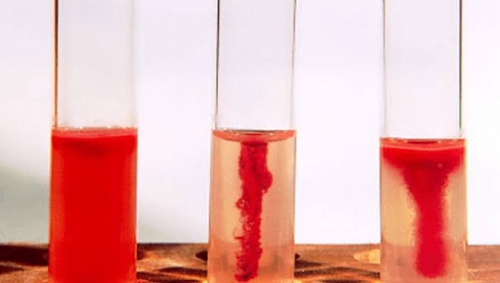
Motility Test
~0.4 mins read
Motility is the ability of an organism to move by itself by means of propeller like flagella unique to bacteria or by special fibrillation that produce a gliding form of motility.
Its principle; motility by bacterium is mostly demonstrated in a semi solid agar medium, in the medium, bacteria swam and give a diffuse spreading growth easily recognized by the naked eye. The medium used is sim medium(sulphide indo motility medium) which is a combination differential medium that test for Sulphur reduction, indo production and motility.
The medium has a very soft consistency that allows mobile bacteria to migrate readily through them causing cloudiness.
profile/7350IMG_20200427_212430.jpg
Justin
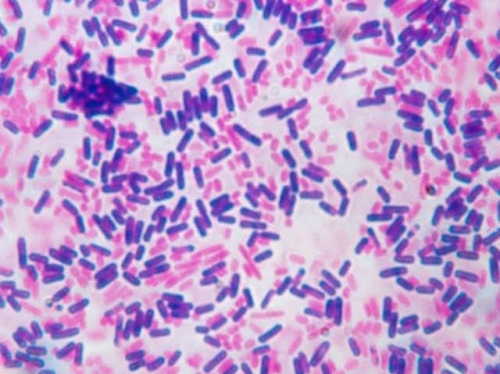
Gram Staining
~0.2 mins read
This is a laboratory procedure used to differentiate between gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Materials use for the procedure includes ; crystal violet(primary stain), gram's iodine(mordant), 95% Ethanol(decolorizer), safranin(secondary stain).
If the laboratory procedure yields a purple colouration the bacteria is Gram positive but if it yields a red or pink colouration the bacteria is Gram negative.
Advertisement

Link socials
Matches
Loading...
