profile/9187IMG_20220713_093816.jpg.webp
Guntu
Birth Control And Family Planning
~4.9 mins read
Birth control and family planning
Your choice of a birth control method depends on a number of factors, including your health, how often you have sex, and whether or not you want children.
Information
Here are some questions to consider when selecting a birth control method:
How well does the method prevent pregnancy? To tell how well a method works, look at the number of pregnancies in 100 women using that method over a period of 1 year.
What are your feelings about getting pregnant? Would an unplanned pregnancy create hardship or distress to a woman or her partner? Or would a pregnancy be welcomed if it occurred earlier than planned?
How much does a method of birth control cost? Does your insurance plan pay for it?
What are the health risks? Talk about these risks with your health care provider before believing what you hear from others.
Is your partner willing to accept and use a given method of birth control?
Do you want a method that you only need to use when you have sex? Or do you want something that is in place and always working?
Is preventing infections spread by sexual contact important? Many methods do not protect you from sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Condoms are the best choice for preventing STIs. They work best when combined with spermicides.
Availability: Can the method be used without a prescription, a provider visit, or, in the case of minors, parental consent?
BARRIER METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
CONDOMS:

A condom is a thin latex or polyurethane sheath. The male condom is placed around the erect penis. The female condom is placed inside the vagina before intercourse.
A condom must be worn at all times during intercourse to prevent pregnancy.
Condoms can be bought in most drug and grocery stores. Some family planning clinics offer free condoms. You do not need a prescription to get condoms.
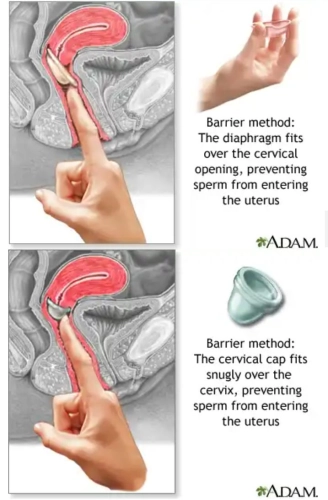
DIAPHRAGM AND CERVICAL CAP:

A diaphragm is a flexible rubber cup that is filled with spermicidal cream or jelly.
It is placed into the vagina over the cervix before intercourse, to prevent sperm from reaching the uterus.
It should be left in place for 6 to 8 hours after intercourse.
Diaphragms must be prescribed by a woman's provider. The provider will determine the correct type and size of diaphragm for the woman.
About 5 to 20 pregnancies occur over 1 year in 100 women using this method, depending on proper use.
A similar, smaller device is called a cervical cap.
Risks include irritation and allergic reactions to the diaphragm or spermicide, and increased frequency of urinary tract infection and vaginal yeast infection. In rare cases, toxic shock syndrome may develop in women who leave the diaphragm in too long. A cervical cap may cause an abnormal Pap test.
VAGINAL SPONGE:
Vaginal contraceptive sponges are soft, and contain a chemical that kills or "disables" sperm.
The sponge is moistened and inserted into the vagina, to cover over the cervix before intercourse.
The vaginal sponge can be bought at your pharmacy without a prescription.
HORMONAL METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
Some birth control methods use hormones. They will have either both an estrogen and a progestin, or a progestin alone. You need a prescription for most hormonal birth control methods.
Both hormones prevent a woman's ovary from releasing an egg during her cycle. They do this by affecting the levels of other hormones the body makes.
Progestins help prevent sperm from making their way to the egg by making mucus around a woman's cervix thick and sticky.

Types of hormonal birth control methods include:
Birth control pills: These may contain both estrogen and progestin, or only progestin.
Implants: These are small rods implanted beneath the skin. They release a continuous dose of hormone to prevent ovulation.
Progestin injections, such as Depo-Provera, that are given into the muscles of the upper arm or buttocks once every 3 months.
The skin patch, such as Ortho Evra, is placed on your shoulder, buttocks, or other place on the body. It releases a continuous dose of hormones.
The vaginal ring, such as NuvaRing, is a flexible ring about 2 inches (5 centimeters) wide. It is placed into the vagina. It releases the hormones progestin and estrogen.
Emergency (or "morning after") contraception: This medicine can be bought without a prescription at your drugstore.
IUD (INTRAUTERINE DEVICE):

The IUD is a small plastic or copper device placed inside the woman's uterus by her provider. Some IUDs release small amounts of progestin. IUDs may be left in place for 3 to 10 years, depending on the device used.
IUDs can be placed at almost any time.
IUDs are safe and work well. Fewer than 1 out of 100 women per year will get pregnant using an IUD.
IUDs that release progestin may be for treating heavy menstrual bleeding and reducing cramps. They may also cause periods to stop completely.
PERMANENT METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
These methods are best for men, women, and couples who feel certain they do not want to have children in the future. They include vasectomy and tubal ligation. These procedures can sometimes be reversed if a pregnancy is desired at a later time. However, the success rate for reversal is not high.

BIRTH CONTROL METHODS THAT DO NOT WORK VERY WELL
Withdrawal of the penis from the vagina before ejaculation can still result in pregnancy. Some semen often escapes before full withdrawal. It can be enough to cause a pregnancy.
Douching shortly after sex is not likely to work. The sperm can make their way past the cervix within 90 seconds. Douching is never recommended because it can cause infections in the uterus and tubes.
Breastfeeding: Despite the myths, women who are breastfeeding can become pregnant.
profile/9187IMG_20220713_093816.jpg.webp
Guntu

11 Best Foods To Boost Your Brain And Memory
~7.8 mins read
11 Best Foods to Boost Your Brain and Memory

Written by Kerri-Ann Jennings, MS, RD — Medically reviewed by Kathy W. Warwick, R.D., CDE, Nutrition — Updated on June 21, 2021
Your brain is kind of a big deal.
As the control center of your body, it’s in charge of keeping your heart beating and lungs breathing and allowing you to move, feel, and think.
That’s why it’s a good idea to keep your brain in peak working condition.
The foods you eat play a role in keeping your brain healthy and can improve specific mental tasks, such as memory and concentration.
Share on PinterestAlexander Spatari/Getty Images
This article lists 11 foods that boost your brain.
1. Fatty fish
When people talk about brain foods, fatty fish is often at the top of the list.
This type of fish includes salmon, trout, albacore tuna, herring, and sardines, all of which are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids (1Trusted Source).
About 60% of your brain is made of fat, and half of that fat is comprised of omega-3 fatty acids (2Trusted Source).
Your brain uses omega-3s to build brain and nerve cells, and these fats are essential for learning and memory (2Trusted Source, 3Trusted Source).
Omega-3s also offer several additional benefits for your brain.
For one thing, they may slow age-related mental decline and help ward off Alzheimer’s disease (4Trusted Source, 5Trusted Source, 6Trusted Source, 7Trusted Source).
On the flip side, not getting enough omega-3s is linked to learning impairments, as well as depression (3Trusted Source, 8Trusted Source).
In general, eating fish seems to have positive health benefits.
Some research also suggests that people who eat fish regularly tend to have more gray matter in their brains. Gray matter contains most of the nerve cells that control decision making, memory, and emotion (9Trusted Source).
Overall, fatty fish is an excellent choice for brain health.
SUMMARY
Fatty fish is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, a major building block of the brain. Omega-3s play a role in sharpening memory and improving mood, as well as protecting your brain against cognitive decline.
2. Coffee
If coffee is the highlight of your morning, you’ll be glad to hear that it’s good for you.
Two main components in coffee — caffeine and antioxidants — can help support brain health.
The caffeine found in coffee has a number of positive effects on the brain, including (10Trusted Source):
Increased alertness. Caffeine keeps your brain alert by blocking adenosine, a chemical messenger that makes you feel sleepy (11Trusted Source, 12Trusted Source).
Improved mood. Caffeine may also boost some of your “feel-good” neurotransmitters, such as dopamine (13Trusted Source).
Sharpened concentration. One study found that caffeine consumption led to short-term improvements in attention and alertness in participants completing a cognition test (14Trusted Source).
Drinking coffee over the long-term is also linked to a reduced risk of neurological diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. The largest risk reduction was seen in those adults who consumes 3-4 cups daily (10Trusted Source, 15Trusted Source).
This could at least be partly due to coffee’s high concentration of antioxidants (16Trusted Source).
SUMMARY
Coffee can help boost alertness and mood. It may also offer some protection against Alzheimer’s, thanks to its content of caffeine and antioxidants.
3. Blueberries
Blueberries provide numerous health benefits, including some that are specifically for your brain.
Blueberries and other deeply colored berries deliver anthocyanins, a group of plant compounds with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (17Trusted Source).
Antioxidants act against both oxidative stress and inflammation, conditions that can contribute to brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases (18Trusted Source).
Some of the antioxidants in blueberries have been found to accumulate in the brain and help improve communication between brain cells (17Trusted Source, 19Trusted Source).
According to one review of 11 studies, blueberries could help improve memory and certain cognitive processes in children and older adults (20Trusted Source).
Try sprinkling them over your breakfast cereal, adding them to a smoothie, or enjoying as is for a simple snack.
SUMMARY
Blueberries are packed with antioxidants that may delay brain aging and improve memory.
4. Turmeric
Turmeric has generated a lot of buzz recently.
This deep-yellow spice is a key ingredient in curry powder and has a number of benefits for the brain.
Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, has been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier, meaning it can directly enter the brain and benefit the cells there (21Trusted Source).
It’s a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound that has been linked to the following brain benefits:
May benefit memory. Curcumin may help improve memory in people with Alzheimer’s. It may also help clear the amyloid plaques that are a hallmark of this disease (21Trusted Source, 22Trusted Source).
Eases depression. Curcumin boosts serotonin and dopamine, both of which improve mood. One review found that curcumin could improve symptoms of depression and anxiety when used alongside standard treatments in people diagnosed with depression (23Trusted Source, 24Trusted Source).
Helps new brain cells grow. Curcumin boosts brain-derived neurotrophic factor, a type of growth hormone that helps brain cells grow. It may help delay age-related mental decline, but more research is needed (25Trusted Source, 26Trusted Source).
Keep in mind that most studies use highly concentrated curcumin supplements in doses ranging from 500–2,000 mg per day, which is much more curcumin than most people typically consume when using turmeric as a spice. This is because turmeric is only made up of around 3–6% curcumin (27Trusted Source).
Therefore, while adding turmeric to your food may be beneficial, you may need to use a curcumin supplement under a doctor’s guidance to obtain the results reported in these studies.
SUMMARY
Turmeric and its active compound curcumin have strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits, which help the brain. In research, it has reduced symptoms of depression and Alzheimer’s disease.
5. Broccoli
Broccoli is packed with powerful plant compounds, including antioxidants (28Trusted Source).
It’s also very high in vitamin K, delivering more than 100% of the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) in a 1-cup (160-gram) serving of cooked broccoli (29Trusted Source).
This fat-soluble vitamin is essential for forming sphingolipids, a type of fat that’s densely packed into brain cells (30Trusted Source).
A few studies in older adults have linked a higher vitamin K intake to better memory and cognitive status (31Trusted Source, 32Trusted Source).
Beyond vitamin K, broccoli contains a number of compounds that give it anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which may help protect the brain against damage (33Trusted Source).
SUMMARY
Broccoli contains a number of compounds that have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, including vitamin K.
6. Pumpkin seeds
Pumpkin seeds contain powerful antioxidants that protect the body and brain from free-radical damage (34).
They’re also an excellent source of magnesium, iron, zinc, and copper (35Trusted Source).
Each of these nutrients is important for brain health:
Zinc. This element is crucial for nerve signaling. Zinc deficiency has been linked to many neurological conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and Parkinson’s disease (36Trusted Source, 37Trusted Source, 38Trusted Source).
Magnesium. Magnesium is essential for learning and memory. Low magnesium levels are linked to many neurological diseases, including migraine, depression, and epilepsy (39Trusted Source, 40Trusted Source).
Copper. Your brain uses copper to help control nerve signals. And when copper levels are out of whack, there’s a higher risk of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s (41Trusted Source, 42Trusted Source.
Iron. Iron deficiency is often characterized by brain fog and impaired brain function (43Trusted Source).
The research focuses mostly on these micronutrients, rather than pumpkin seeds themselves. However, since pumpkin seeds are high in these micronutrients, you can likely reap their benefits by adding pumpkin seeds to your diet.
SUMMARY
Pumpkin seeds are rich in many micronutrients that are important for brain function, including copper, iron, magnesium, and zinc.
The 5 Best Foods to Eat When You’re Sick
0 seconds of 1 minute, 11 seconds
Watch More
7. Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate and cocoa powder are packed with a few brain-boosting compounds, including flavonoids, caffeine, and antioxidants.
Dark chocolate has a 70% or greater cocoa content. These benefits are not seen with regular milk chocolate, which contains between 10–50% cocoa.
Flavonoids are a group of antioxidant plant compounds.
The flavonoids in chocolate gather in the areas of the brain that deal with learning and memory. Researchers believe that these compounds may enhance memory and also help slow down age-related mental decline (44, 45Trusted Source, 46)Trusted Source.
In fact, a number of studies back this up (47Trusted Source, 48Trusted Source, 49Trusted Source).
According to one study in over 900 people, those who ate chocolate more frequently performed better in a series of mental tasks, including some involving memory, compared with those who rarely ate it (50Trusted Source).
Chocolate is also a legitimate mood booster, according to research.
One study found that participants who ate chocolate experienced increased positive feelings compared to those who ate crackers (51Trusted Source).
However, it’s still not clear whether that’s because of compounds in the chocolate or simply because the tasty flavor makes people happy.
SUMMARY
The flavonoids in chocolate may help protect the brain. Studie
Advertisement

Link socials
Matches
Loading...
