EntertainmentNews And PoliticsPersonal Care And BeautyHealth And LifestyleOthersMotivationalsSports And FitnessNewsHealthCelebrityIT And Computer ScienceStoriesScience And TechnologyBusiness And MoneyGeneralTechnologyBeautyQuestions And AnswersAgricultureArts And EducationFitnessPoliticsBusinessLifetipsSportsLifestyleEducationMotivationFamily And HolidaysReligion And Principles
DemuchGS
Computer Scientist : Am A Skillful Person, I Love Advertising And I Am Into Blogging, Am A Content Creator, IG: Demuchgs, Facebook: Demuch Spacial, Page: Official Demuch
Wants to meet Just Friends
Articles
561
Followers
32
profile/919images-01.jpeg
DemuchGS

3 Surprising Reasons For A Headache
~2.1 mins read
1. The smell of perfume, paint or gasoline
People prone to migraines often have heightened sensitivity to a number of senses, including smell, sound and sight. That’s why the smell of perfume, paint or gasoline can bring on a migraine. The migraine brain is sensitive to all kinds of environmental and bodily changes, which includes extreme weather, alcohol and particular foods, and even certain hairstyles. “It’s not that people prone to migraine have only one trigger,” says Rami Burstein, a professor of anesthesia and neuroscience at Harvard Medical School. He adds that when people have recurring headaches, their brains can become attuned to — and at the mercy of — unusual environmental changes, such as weather, or too much sleep or too little. Any deviation from the normal pattern of events can set a migraine sufferer into an attack. In other words, even the subtlest incident can be a trigger.
For relief: Burstein suggests that those prone to migraines find any and every possible way to avoid common triggers. For some, this may mean requesting — and advocating for — a workplace fragrance policy that restricts the use of scented products.
2. Weather patterns
A change in barometric pressure or atmospheric pressure (such as altitude) can trigger a headache attack through changes in the area of the brain that controls pain. External pressure changes may also change the pressure within the sinuses and inner ears, intensifying the experience of pain for those who are predisposed to such sensitivities. Gray skies, high humidity, rising temperatures and storms are common pressure changers. People commonly complain that summer weather can trigger migraines, according to the Mayo Clinic. Sunlight glare, high humidity, extreme heat and dry air are possible triggers. Dehydration can also cause headaches.
For relief: Keep a headache or migraine diary, jotting down any changes in the weather, such as rainstorms, wind or increased humidity. Once you establish a relationship between weather and your migraines, you can potentially pretreat them with the appropriate medication.
3. Aged and fermented foods
In some people, tyramine, a naturally occurring substance found in aged cheeses, smoked fish, cured meats, bacon and some types of beer and wine, is thought to trigger migraines. Tyramine has long been a scapegoat for dietary-induced migraine, but research is not conclusive. A small number of people with headaches are affected by tyramine. Not only are food triggers rare, but they are sporadic. “When food triggers migraines it’s inconsistent, sometimes yes and sometimes no,” Burstein says. Brandes has found that among her patients, the biggest culprit of food or drink triggers is alcohol.
For relief: If you do think there’s an alcohol-migraine connection at play, note that beer, especially tap or home-brewed beer, red wine, vermouth, sherry and some liqueurs all have high amounts of tyramine. See if switching over to white wine or spirits such as rum, vodka or gin is less of a migraine trigger. If that doesn’t work, consider limiting or omitting alcohol.
profile/919images-01.jpeg
DemuchGS
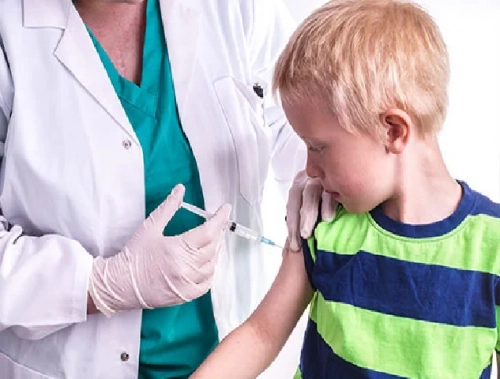
Do You Need A Tetanus Shot?
~2.1 mins read
What is tetanus?
Tetanus, sometimes called lockjaw, is a rare disease caused by bacteria known as Clostridium tetani. A toxin produced by the bacteria affects the function of the nerves and leads to severe muscle spasms in the abdomen, neck, stomach, and extremities.
The bacteria that cause tetanus can be found in soil, manure, or dust. They infect humans by entering the body through cuts or puncture wounds, particularly when the wound area is dirty. Animal bites, burns, and non-sterile injection of drugs can also lead to infection with Clostridium tetani. The first symptoms of tetanus can appear any time from 3 days to weeks after infection, but the average time until symptom onset is 8 days. Tetanus is not contagious, so you cannot acquire the disease from someone who has it.
Advertisement

Link socials
Matches
Loading...
